Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Baba, Yuji*; Shimoyama, Iwao
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 987, p.164845_1 - 164845_5, 2021/01
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:34.88(Instruments & Instrumentation)Multi-atom resonance (MAR) effect following the core-level resonant photoexcitation has been investigated for simple binary compounds such as CaCl , KCl and SrCl
, KCl and SrCl . For solid CaCl
. For solid CaCl , it was found that the intensity of Cl K
, it was found that the intensity of Cl K X-rays was reduced when the energy of the incident X-rays was tuned at the resonance energy of the neighboring Ca K-edge, but such intensity reduction was not observed for aqueous solution of CaCl
X-rays was reduced when the energy of the incident X-rays was tuned at the resonance energy of the neighboring Ca K-edge, but such intensity reduction was not observed for aqueous solution of CaCl . Similar results were also obtained for the KCl and SrCl
. Similar results were also obtained for the KCl and SrCl . From these results, it was clarified that for these binary compounds, the multi-atom resonance does occur only in an atom that is directly bound to the excited atom.
. From these results, it was clarified that for these binary compounds, the multi-atom resonance does occur only in an atom that is directly bound to the excited atom.
Rizaal, M.; Saito, Takumi*; Okamoto, Koji*; Erkan, N.*; Nakajima, Kunihisa; Osaka, Masahiko
Mechanical Engineering Journal (Internet), 7(3), p.19-00563_1 - 19-00563_10, 2020/06
The adsorption of cesium (Cs) on calcium silicate insulation of primary piping system is postulated to contribute in high dose rate of surrounding pedestal area in Fukushima Daiichi NPP unit 2. In this study, room-temperature experiment of Cs adsorption on calcium silicate has been studied as an initial approach of Cs adsorption behavior toward higher temperature condition. As the result of analyzing of Cs adsorption kinetics, it was expected that the underlying adsorption mechanism is chemisorption. Furthermore, analysis of adsorption isotherm suggested unrestricted monolayer formation followed by multilayer formation.
 C based on two binary non-ideal solid solutions
C based on two binary non-ideal solid solutionsWalker, C.; Suto, Shunkichi; Oda, Chie; Mihara, Morihiro; Honda, Akira
Cement and Concrete Research, 79, p.1 - 30, 2016/01
Times Cited Count:69 Percentile:90.65(Construction & Building Technology)Modeling the solubility behavior of calcium silicate hydrate (C-S-H) gel is important to make quantitative predictions of the degradation of hydrated ordinary Portland cement (OPC) based materials. Experimental C-S-H gel solubility data have been compiled from the literature, critically evaluated and supplemented with new data from the current study for molar Ca/Si ratios = 0.2-0.83. All these data have been used to derive a discrete solid phase (DSP) type C-S-H gel solubility model based on two binary non-ideal solid solutions in aqueous solution(SSAS). Features of the DSP type C-S-H gel solubility model include satisfactory predictions of pH values and Ca and Si concentrations for all molar Ca/Si ratios = 2.7  0 in the C-S-H system, portlandite (CH) for Ca/Si ratios
0 in the C-S-H system, portlandite (CH) for Ca/Si ratios  1.65, congruent dissolution at Ca/Si ratios = 0.85, and amorphous silica (SiO
1.65, congruent dissolution at Ca/Si ratios = 0.85, and amorphous silica (SiO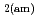 ) for Ca/Si ratios
) for Ca/Si ratios  0.55 as identified in the current study by IR spectroscopy.
0.55 as identified in the current study by IR spectroscopy.
Suzuki, Hiroshi; Bae, S.*; Kanematsu, Manabu*
Advances in Materials Science and Engineering, 2016, p.8936084_1 - 8936084_6, 2016/00
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:7.58(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The deformation behavior of nanostructure of calcium silicate hydrate (CSH) in Portland cement (PC) paste under compression was successfully characterized by the atomic pair distribution function (PDF) measured by using Synchrotron X-rays. The PDF of the PC paste showed a unique deformation behavior for a short range order below 2.0 nm in radius corresponding to the size of the CSH particle (globule), while the deformation for a long range order was similar to that of a calcium hydroxide phase measured by the diffraction peak shift. The compressive deformation of the CSH nanostructure can be divided into three stages with different interactions between globules. This behavior would originate from the granular nature of CSH which deforms with increasing packing density by slipping the interfaces between globules, rearranging the overall CSH nanostructure. This study will lead to increasing applications of the PDF technique to provide clues for understanding the deformation mechanism of CSH in PC paste.
Maeda, Toshikatsu; Bamba, Tsunetaka*; Hotta, Katsutoshi*; Mizuno, Tsuyoshi*; Ozawa, Tatsuya
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 4(4), p.242 - 247, 2005/12
no abstracts in English
 Ca ionization potential by high-precision three-step resonance ionization spectroscopy
Ca ionization potential by high-precision three-step resonance ionization spectroscopyMiyabe, Masabumi; Oba, Masaki; Kato, Masaaki; Wakaida, Ikuo; Watanabe, Kazuo
JAERI-Research 2004-023, 17 Pages, 2004/11
High precision resonance ionization spectroscopy has been applied to determination of an accurate ionization potential of  Ca. Three-step resonant excitation with single-mode extended cavity diode lasers populates a series of
Ca. Three-step resonant excitation with single-mode extended cavity diode lasers populates a series of 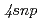 (
( P
P ) and
) and 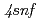 (
( F
F ) Rydberg states in the rage of
) Rydberg states in the rage of  =20-150. By using an extended Ritz formula for quantum defect, the series convergence limit has been determined to be 49305.9240 (20) cm
=20-150. By using an extended Ritz formula for quantum defect, the series convergence limit has been determined to be 49305.9240 (20) cm with the accuracy improved one order of magnitude higher than previously reported ones.
with the accuracy improved one order of magnitude higher than previously reported ones.
Wakaida, Ikuo; Miyabe, Masabumi
Bunseki, 2004(10), p.585 - 590, 2004/10
no abstracts in English
*; Mihara, Morihiro;
JNC TN8430 2001-007, 56 Pages, 2002/01
In the geological disposal concept of radioactive wastes, a kind of clay with sorption ability and low permeability, called bentonite, is envisaged as an engineered barrier system in the geological repository. Also, the cemetitious material is envisaged as the backfill material in the vaults and the structure material of the vaults. The groundwater in contact with the cementitious material will promote hyperalkaline conditions in the repository environment and these conditions will affect the performance of the bentonite. Therefore, it is necessary to investigate the interaction between the cementitious material and the bentonite for the evaluation of long term stability of the disposal system. In this study, for the identification and the investigation of the secondary minerals, the batch immersion experiments of the powder bentonite were carried out using synthetic cement leachates (pH=7, 12.5, 14) at 200 C. As the results, it was confirmed that Na as exchangeable cations in the bentonite can exchange relatively easily with Ca in the solution from the experiment results. And the ratio of cation exchange was estimated to be about 25% based on the amount of exchangeable cations Ca
C. As the results, it was confirmed that Na as exchangeable cations in the bentonite can exchange relatively easily with Ca in the solution from the experiment results. And the ratio of cation exchange was estimated to be about 25% based on the amount of exchangeable cations Ca between layers. Furthermore, it was concretely shown that the generation of analcime might be affected by the Na concentration from results of the solution analyses and a stability analysis of analcime using the chemical equilibrium model, in addition to the pH in the solution.
between layers. Furthermore, it was concretely shown that the generation of analcime might be affected by the Na concentration from results of the solution analyses and a stability analysis of analcime using the chemical equilibrium model, in addition to the pH in the solution.
 -isopropylacrylamide)/potassium chloride gel electrolytes
-isopropylacrylamide)/potassium chloride gel electrolytesChen, J.; Maekawa, Yasunari; Yoshida, Masaru; Tsubokawa, Norio*
Journal of Polymer Science, Part B; Polymer Physics, 40, p.134 - 141, 2001/11
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:27.52(Polymer Science)no abstracts in English
 -isopropylacrylamide and calcium chloride
-isopropylacrylamide and calcium chlorideChen, J.; Yoshida, Masaru; Maekawa, Yasunari; Tsubokawa, Norio*
Polymer, 42(23), p.9361 - 9365, 2001/11
Times Cited Count:31 Percentile:72.25(Polymer Science)no abstracts in English
 Pu
Pu )TiO
)TiO (x=0 and 0.20)
(x=0 and 0.20)Sato, Tsuyoshi*; Yamazaki, Satoshi*; Yamashita, Toshiyuki; Matsui, Tsuneo*; Nagasaki, Takanori*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 294(1-2), p.135 - 140, 2001/04
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:19.66(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
JNC TN8400 2001-008, 36 Pages, 2001/03
Research on geologic disposal of high-level radioactive waste(HLW) has been underway in many countries. Bentonite exhibiting a low permeability, high swelling property and high sorption capacity for many radioelements is proposed as a buffer material in many countlies. Recently, cementitious materials are considered as candidate matelials for the geologic disposal of high-level radioactive waste. As the pH and the Ca, Na, K contents of hyperalkaline pore water from the cementitious materials are high, this hyperalkaline pore water would alter the buffer material. The main aim of this study is to investigate the effect of alkaline pore water into the bentonite. Used materials are montmorillonite, albite and quartz composing bentonite. These minerals mixed in a constant ratio (1:1wt%) made to react to distilled water and the alkali solutions (pH11-13). These studies have been conducted at temperatures of 50 - 150 C and run times of 10 - 200 day. XRD(X-ray powder diffraction) and SEM (Scanning Electron Microscopy) analyses were applied to studying the structure and quantitative data of each sample. From the result of this study, the main formed mineral of this experiment was analcime, which showed the tendency with a large amount of generation at a higher pH and temperature. Quantitative data of this study was conducted by X-ray powder diffraction method. THe order of the amount of the second analcime in each experiment is shown in the following. Montmorillonite and albite mixing test
C and run times of 10 - 200 day. XRD(X-ray powder diffraction) and SEM (Scanning Electron Microscopy) analyses were applied to studying the structure and quantitative data of each sample. From the result of this study, the main formed mineral of this experiment was analcime, which showed the tendency with a large amount of generation at a higher pH and temperature. Quantitative data of this study was conducted by X-ray powder diffraction method. THe order of the amount of the second analcime in each experiment is shown in the following. Montmorillonite and albite mixing test  Montmorillonite test
Montmorillonite test  Montmorillonite and quartz mixing test Activation energies (E
Montmorillonite and quartz mixing test Activation energies (E ) using the quantitative data of each test are shown in the following. (1)Montmorillonite test : 54.9kJ/mol (2)Montmorillonite and albite mixing test : 51.9kJ/mol (3)Montmorillonite and quartz mixing test : 59.6kJ/mol
) using the quantitative data of each test are shown in the following. (1)Montmorillonite test : 54.9kJ/mol (2)Montmorillonite and albite mixing test : 51.9kJ/mol (3)Montmorillonite and quartz mixing test : 59.6kJ/mol
Iriya, Keishiro*; *; Fujita, Hideki*; Kubo, Hiroshi*
JNC TJ8400 2000-034, 212 Pages, 2000/02
Cementious materials and highly compacted bentnite are expectable candidates as materials of TRU waste repositories. It was pointed out that Bentonite might be changed to Zeolite and surrounding rock might be altered by high alkalinity water flow, since cement hydrate leached to pore water of cement and it was changed to alkaline. Transportation of radio-nuclides might be accelerated by organic materials, such as super plasticizer, and nitlate which is contained in nuclear wastes. It was concluded by previous studies that rock and bentonite is stable in alkaline water which pH is less than 10.5. The new type of low alkalinity cement with high silica fume and fly ash content which could keep pH below 11.0 was developed and its performance has been assessed. However since Zeolitation and ilitation were reported upon deterioration of bentonite bated in certain condition, it should be assessed by long term experiment. Since Capacity of keeping integrity of bentonite hasn't been directly checked by experiments upon the developed new type of low alkalinity cement it should be done. Although amount of leaching organic was quantitatively and experimentally assessed at an early age, effect of changing of amount and shape hasn't assessed in leaching of radio nuclides. Although it is pointed out that deterioration of cementitious materials isn't accelerated by condensed nitrate solution at early period after closure, it is considered that it might be accelerated corresponding to chemical composition in case of decrement of concentration of nitrate. In this study, deterioration of materials will be assessed in detail in order to feed back the results to assessment of transportation of radio nuclides. Long term deterioration of bentonite by leaching water of cement will be experimentally assessed, and deteriorating test of bentonite will be carried out by leaching water of low alkalinity cement. Amount of organic and component of it will be measured. Furthermore ...
Iriya, Keishiro*; *; Kubo, Hiroshi*; Fujita, Hideki*
JNC TJ8400 2000-033, 95 Pages, 2000/02
Cementious materials and highly compacted bentnite are expectable candidates as materials of TRU waste repositories. It was pointed out that Bentonite might be changed to Zeolite and surrounding rock might be altered by high alkalinity water flow, since cement hydrate leached to pore water of cement and it was changed to alkaline. Transportation of radio-nuclides might be accelerated by organic materials, such as super plasticizer, and nitrate which is contained in nuclear wastes. It was concluded by previous studies that rock and bentonite is stable in alkaline water which pH is less than 10.5. The new type of low alkalinity cement with high silica fume and fly ash content which could keep pH below 11.0 was developed and its performance has been assessed. However since Zeolitation and ilitation were reported upon deterioration of bentonite bated in certain condition, it should be assessed by long term experiment. Since Capacity of keeping integrity of bentonite hasn't been directly checked by experiments upon the developed new type of low alkalinity cement it should be done. Although amount of leaching organic was quantitatively and experimentally assessed at an early age, effect of changing of amount and shape hasn't assessed in leaching of radio nuclides. Although it is pointed out that deterioration of cementitious materials isn't accelerated by condensed nitrate solution at early period after closure, it is considered that it might be accelerated corresponding to chemical composition in case of decrement of concentration of nitrate. In this study, deterioration of materials will be assessed in detail in order to feed back the results to assessment of transportation of radio nuclides. Long term deterioration of bentonite by leaching water of cement will be experimentally assessed, and deteriorating test of bentonite will be carried out by leaching water of low alkalinity cement. Amount of organic and component of it will be measured. Furthermore ...
Imai, Jun*
JNC TJ8400 2000-008, 196 Pages, 2000/02
The objective of this research is to make clear long-term alteration processes of bentonite contacting with concrete under a repository condition for radioactive waste. The Uzu tunnel in yamagata prefecture in Japan, constructed during the term of December of 1963 to July 1967, was selected as an appropriate natural analogue: the tunnel wall was made of portland cement and which has been contacting with a bentonite bed during  32 years. Sample analyses indicated that the original bentonite was Na
32 years. Sample analyses indicated that the original bentonite was Na -type and it changed to Ca
-type and it changed to Ca -type in the range of a few millimeters from the contact. Although a Ca
-type in the range of a few millimeters from the contact. Although a Ca leaching was also observed from the concrete near the contact, neither transformation to zeolite nor to illite was recognized. On the other hand, sulfur increased and ettringite (3CaO
leaching was also observed from the concrete near the contact, neither transformation to zeolite nor to illite was recognized. On the other hand, sulfur increased and ettringite (3CaO  Al
Al O
O
 3CaSO
3CaSO 4
4  32H
32H O) was recognized in the concrete within the depth about 30 mm from the contact.
O) was recognized in the concrete within the depth about 30 mm from the contact.
Tanaka, Satoru*
JNC TJ8400 2000-003, 62 Pages, 2000/02
For the safety assessment of radioactive waste disposal, it is important to elucidate the effect of colloids on radionuclide migration, which are released with dissolution of cementitious materials composing engineered barricr. In the previous work, we identified and characterized the colloidal particles in the solutions contacting cement hydrates, OPC and low-alkaline cement paste, and observed the release of the colloid particle. In the present work, we performed same experiments as the last year to confirm the reproducibility of the colloid release. We studied the leaching behavior of the colloid when OPC and low-alkaline cement past contact water flow. Furthermore, the effect of an alumina particle was studied, which is used as a barrier material for colloid migration. The following conclusions were derived: (1)In the solution contacting cement paste, the small amount of particles, which are considered as CaCO or silicate colloids were observed. Thus, the reproducibility of the last work was confirmed. (2)The leaching of colloid in the solution was confirmed by water flow through the cement paste. The concentration of particle was as low as 10
or silicate colloids were observed. Thus, the reproducibility of the last work was confirmed. (2)The leaching of colloid in the solution was confirmed by water flow through the cement paste. The concentration of particle was as low as 10
 10
10 mL
mL . (3)Al
. (3)Al 0
0 powder, with the diameter of 200
powder, with the diameter of 200 150
150 m, was found to be effective to some extent as a barrier for a colloid migration from low-alkaline cement paste.
m, was found to be effective to some extent as a barrier for a colloid migration from low-alkaline cement paste.
 under high-temperature and high-pressure conditions
under high-temperature and high-pressure conditionsFukui, Hiroyuki*; Otaka, Osamu*; Katsura, Tomoo*; Nagai, Takaya*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Utsumi, Wataru; Kikegawa, Takumi*
Science and Technology of High Pressure, p.554 - 557, 2000/00
no abstracts in English
Mihara, Morihiro; ; Ueta, Shinzo*; *
JNC TN8430 99-011, 27 Pages, 1999/11
In radioactive waste disposal, compacted Na-bentonite has been proposed for a buffer material. However, Na-bentonite would change to Ca-bentonite in the long term period. The change of Na-bentonite to Ca-bentonite might cause the change in the data concerning with nuclides migration properties such as permeability, sorption and diffusion. In this study, effective diffusion coefficients of HTO, Cs, I and C in compacted Ca-bentonite which was changed from Na-bentonite, Kunigel V1, were obtained and were compared to published those of Kunigel V1. In addition, effective diffusion coefficients for compacted Ca-bentonite with syncetic sea system water, SW, were obtained in order to investigate effect of solution composition. The magnitude of effective diffusion coefficients in Ca-bentonite are arranged in smaller order as Cs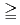 HTO
HTO I
I C. It is estimated that their effective diffusion coefficients are same those of Na-bentonite. About effect of solution composition, effective diffusion coefficients of HTO in 1.8g/cm
C. It is estimated that their effective diffusion coefficients are same those of Na-bentonite. About effect of solution composition, effective diffusion coefficients of HTO in 1.8g/cm dry density with SW were almost same values with distilled system water, DW. However, effective diffusion coefficients of HTO in lower density were smaller than values with DW. Regarding as effective diffusion coefficients of Cs in 1.8g/cm
dry density with SW were almost same values with distilled system water, DW. However, effective diffusion coefficients of HTO in lower density were smaller than values with DW. Regarding as effective diffusion coefficients of Cs in 1.8g/cm dry density, the effect of SW could not be observed as well as HTO. However, effective diffusion coefficients of I and C existing as an anion in pore water of bentonite increased by the reduction in the ion exclusion.
dry density, the effect of SW could not be observed as well as HTO. However, effective diffusion coefficients of I and C existing as an anion in pore water of bentonite increased by the reduction in the ion exclusion.
Sasamoto, Hiroshi; Yui, Mikazu; Arthur, R. C,*
JNC TN8400 99-033, 153 Pages, 1999/07
The results of hydrochemical investigations of groundwaters in the Kurihashi granodiorite at JNC's Kamaishi in-situ tests site indicate that these solutions are: (1)meteoric in origin, (2)chemically reducing (at depths greater than a few hundreds meters), (3)relatively young [residence times in the Kurihashi granodiorite generally less than about 40 years, but groundwaters older than several thousand years BP (before present) are also indicated by preliminary carbon-14 dating of samples obtained from the KH-1 borehole], (4)Ca-HCO type solutions near the surface, changing to Na-HCO
type solutions near the surface, changing to Na-HCO type groundwaters with increasing depth. The evolution of groundwater compositions in the Kurihashi granodiorite is modeled assuming local equilibrium for selected mineral-fluid reactions, taking into account the rainwater origin of these solutions. Results suggest it is possible to interpret approximately the "real" groundwater chemistry (i.e., pH, Eh, total dissolved concentrations of Si, Na, Ca, K, AI, carbonate and sulfate) in the Kurihashi granodiorite if the following assumptions are adopted: (1)CO
type groundwaters with increasing depth. The evolution of groundwater compositions in the Kurihashi granodiorite is modeled assuming local equilibrium for selected mineral-fluid reactions, taking into account the rainwater origin of these solutions. Results suggest it is possible to interpret approximately the "real" groundwater chemistry (i.e., pH, Eh, total dissolved concentrations of Si, Na, Ca, K, AI, carbonate and sulfate) in the Kurihashi granodiorite if the following assumptions are adopted: (1)CO concentration in the gas phase contacting pore solutions in the overlying soil zone = 10
concentration in the gas phase contacting pore solutions in the overlying soil zone = 10 bar, (2)minerals in the rock zone that control the solubility of respective elements in the groundwater include; chalcedony (Si), albite (Na), kaolinite (Al), calcite (Ca and carbonate), microcline (K) and pyrite (Eh and sulfate). Discussions with international experts suggest a systematic approach utilizing reaction-path models of irreversible water-rock interactions in open systems may be needed to more realistically model groundwater evolution at the Kamaishi test site. Detailed information characterizing certain site properties (e.g., fracture mineralogy) may be required to adequately constrain such models, however.
bar, (2)minerals in the rock zone that control the solubility of respective elements in the groundwater include; chalcedony (Si), albite (Na), kaolinite (Al), calcite (Ca and carbonate), microcline (K) and pyrite (Eh and sulfate). Discussions with international experts suggest a systematic approach utilizing reaction-path models of irreversible water-rock interactions in open systems may be needed to more realistically model groundwater evolution at the Kamaishi test site. Detailed information characterizing certain site properties (e.g., fracture mineralogy) may be required to adequately constrain such models, however.